Consumer Units By Size
Find the consumer unit size you require!
Welcome to our comprehensive Consumer Unit by size page, where you'll find diverse consumer units designed to meet your specific electrical requirements. We have meticulously organized our selection by size, making it easier than ever for you to discover the perfect consumer unit for your needs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
What is a Consumer Unit?
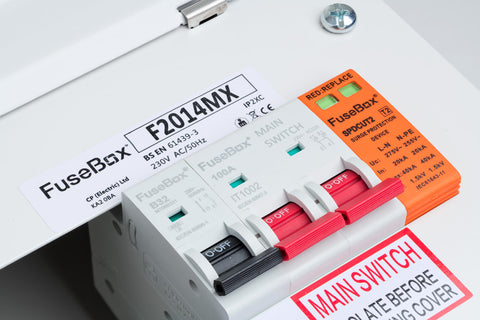
A consumer unit, also known as a distribution board or fuse box, is a crucial component of the electrical supply system in a building or property. It is the main point where electrical power is distributed and controlled to various circuits within the premises. The primary purpose of a consumer unit is to protect the electrical installation from overload, short circuits, and electrical faults, ensuring the safety of occupants and the property.
Key features of a consumer unit include:
-
Main Switch: This is the primary switch that allows you to turn off or on the entire electrical supply to the property. It is used for maintenance, repairs, or during emergencies.
-
Circuit Breakers or RCDs: These are protective devices that automatically trip and disconnect the power supply when they detect faults, such as overloads or short circuits. Circuit breakers protect specific circuits, while Residual Current Devices (RCDs) protect against electric shocks in the event of a fault to earth.
-
Individual Circuit Fuses or Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs): These are devices that protect individual circuits in the building, such as lighting, sockets, or specific appliances. They are rated to handle specific current loads and trip when the current exceeds the rated capacity.
-
Neutral and Earth Terminals: The consumer unit provides connection points for the neutral and earth wires, ensuring safe grounding and completing the electrical circuit.
-
Busbars: These are conductive bars inside the consumer unit that distribute the electrical power to different circuit breakers or fuses.
-
Enclosure: The consumer unit is enclosed within a protective casing made of non-conductive material, providing insulation and protection to the electrical components inside.
Consumer units have evolved over time, and modern units may also include additional features such as surge protection devices, smart monitoring capabilities, and the ability to accommodate renewable energy sources like solar panels.
It's important to note that consumer units should be installed by a qualified electrician to ensure proper and safe wiring, compliance with electrical regulations, and to choose the right unit size and features to meet the specific electrical needs of the property.